Unlocking Superior Sound: How High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) Is Transforming Loudspeaker Enclosure Manufacturing. Discover the Science, Benefits, and Industry Shifts Behind This Material’s Rise.
- Introduction: The Role of Enclosure Materials in Loudspeaker Performance
- What Is High-Density Fiberboard (HDF)? Composition and Properties
- Why HDF? Comparing HDF to MDF, Plywood, and Other Materials
- Acoustic Advantages: How HDF Enhances Sound Quality
- Manufacturing Processes: Working with HDF in Loudspeaker Enclosures
- Durability and Longevity: HDF’s Resistance to Warping and Wear
- Cost Analysis: Is HDF a Smart Investment for Manufacturers?
- Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Sourcing of HDF
- Case Studies: Brands and Products Leveraging HDF for Superior Audio
- Future Trends: Innovations and Emerging Uses of HDF in Audio Engineering
- Conclusion: Is HDF the Future of Loudspeaker Enclosure Manufacturing?
- Sources & References
Introduction: The Role of Enclosure Materials in Loudspeaker Performance
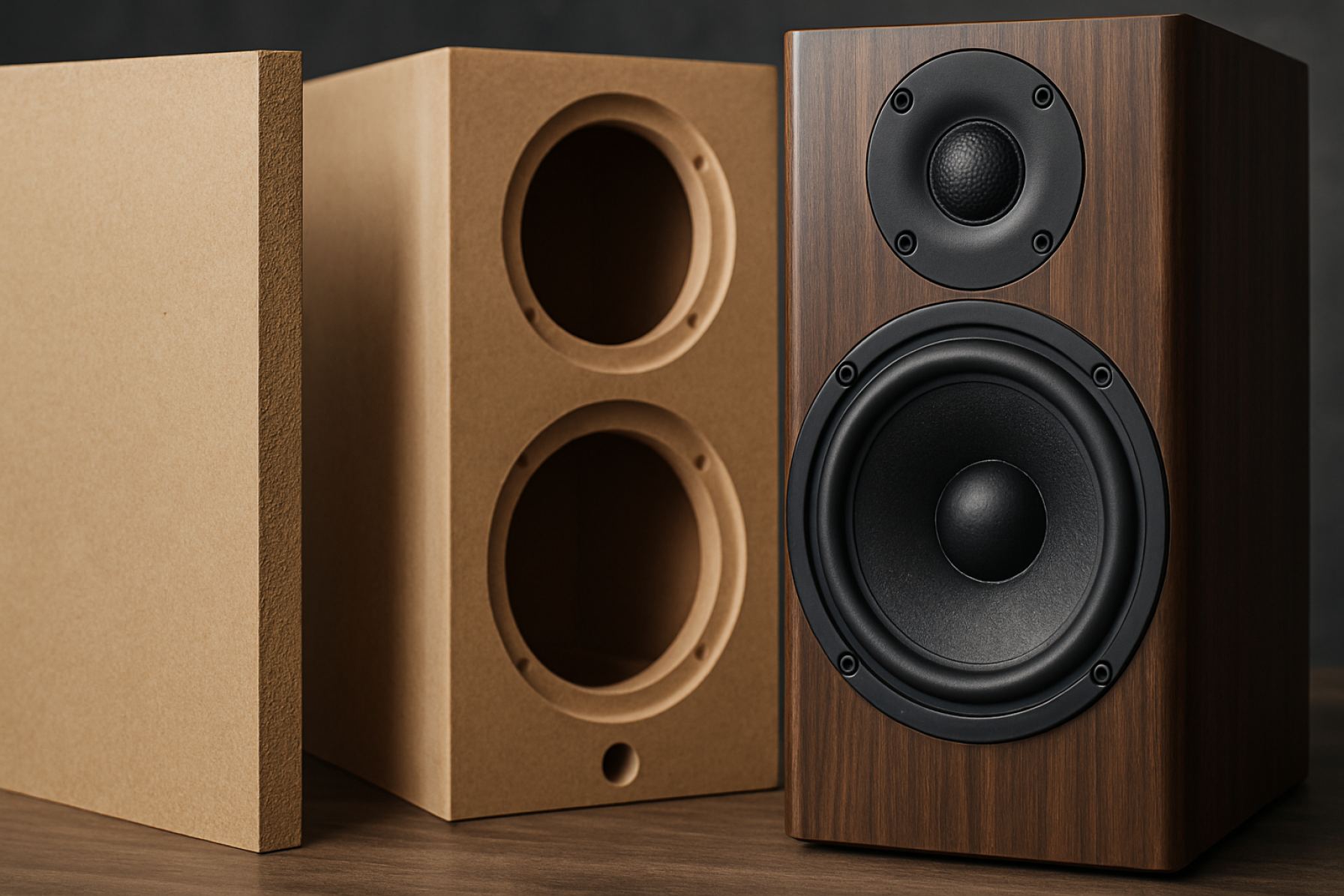
The choice of enclosure material is a critical factor in loudspeaker design, directly influencing acoustic performance, durability, and manufacturing cost. Enclosure materials must provide structural rigidity to minimize unwanted vibrations and coloration, while also being workable for precise construction. Traditionally, materials such as Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF), plywood, and solid wood have been used, each offering a balance of acoustic and practical properties. In recent years, High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) has emerged as a notable alternative, particularly in high-performance and premium loudspeaker applications.
HDF is an engineered wood product characterized by its higher density and finer fiber composition compared to MDF. This results in a material that is not only stronger and more resistant to deformation but also offers superior acoustic damping properties. The increased density of HDF helps to suppress panel resonances and vibrations that can color the sound, thereby enabling more accurate audio reproduction. Additionally, HDF’s smooth surface and uniform structure facilitate precise machining and finishing, which are essential for achieving tight tolerances and aesthetic appeal in loudspeaker enclosures.
The adoption of HDF in loudspeaker manufacturing reflects a broader trend toward optimizing enclosure materials for both sonic and practical benefits. As manufacturers seek to deliver clearer, more faithful sound reproduction, the role of advanced materials like HDF becomes increasingly significant. The following sections will explore the specific advantages, challenges, and applications of HDF in the context of loudspeaker enclosure design and production.
What Is High-Density Fiberboard (HDF)? Composition and Properties
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) is an engineered wood product renowned for its exceptional density, strength, and uniformity. It is manufactured by compressing wood fibers—typically derived from hardwoods—under high pressure and temperature, with the addition of synthetic resins as binders. The result is a panel with a density typically exceeding 800 kg/m³, which is significantly higher than that of Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) and standard particleboard. This high density imparts HDF with superior mechanical properties, including enhanced rigidity, dimensional stability, and resistance to warping or splitting.
The composition of HDF is characterized by a fine, homogeneous fiber structure, which allows for smooth surfaces and precise machining. The absence of voids or grain patterns, common in natural wood, ensures consistent acoustic and structural performance—an essential attribute for loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing. HDF’s closed surface also provides an excellent substrate for veneers, laminates, and paints, facilitating both aesthetic and functional customization.
In terms of acoustic properties, HDF’s mass and rigidity help minimize unwanted panel vibrations and resonance, contributing to clearer sound reproduction in loudspeaker enclosures. Its uniform density ensures predictable behavior under acoustic loads, making it a preferred material for high-fidelity audio applications. Additionally, HDF is less susceptible to moisture absorption compared to other fiberboards, further enhancing its suitability for precision audio equipment. For more detailed technical specifications, refer to Wood Panel Industries Federation and APA – The Engineered Wood Association.
Why HDF? Comparing HDF to MDF, Plywood, and Other Materials
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) is increasingly favored in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing due to its unique combination of density, uniformity, and acoustic properties. When compared to Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF), HDF offers a denser and more homogeneous structure, resulting in improved rigidity and reduced resonance. This is crucial for loudspeaker enclosures, as unwanted vibrations and panel flexing can color the sound and degrade audio fidelity. HDF’s higher density (typically above 800 kg/m³) provides better damping of internal vibrations than MDF, which generally ranges from 600 to 800 kg/m³ The Wood Database.
Plywood, another common material, is valued for its strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to warping. However, its layered construction can introduce inconsistencies in density and internal voids, potentially leading to unpredictable acoustic behavior. In contrast, HDF’s fine, uniform fibers ensure consistent performance across the entire panel, minimizing the risk of acoustic anomalies The Engineering Toolbox.
Other materials, such as particleboard or solid wood, often fall short in terms of dimensional stability and acoustic neutrality. Particleboard is prone to crumbling and lacks the density required for high-fidelity sound reproduction, while solid wood can warp and introduce tonal coloration due to its natural grain structure. HDF’s smooth surface also facilitates precise machining and finishing, allowing for tight tolerances and high-quality aesthetics in loudspeaker design Fine Woodworking.
In summary, HDF’s superior density, uniformity, and machinability make it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking optimal acoustic performance and durability in loudspeaker enclosures.
Acoustic Advantages: How HDF Enhances Sound Quality
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) is widely favored in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing due to its notable acoustic advantages. The material’s dense, uniform structure minimizes unwanted resonances and vibrations that can color or distort audio output. Unlike natural wood, which may have inconsistent grain patterns and internal voids, HDF offers a homogenous composition, ensuring predictable and repeatable acoustic performance across production batches. This consistency is crucial for high-fidelity loudspeakers, where even minor enclosure anomalies can impact sound clarity and tonal balance.
HDF’s high mass and rigidity contribute to its ability to dampen cabinet vibrations. When a loudspeaker operates, the enclosure must remain as inert as possible to prevent it from radiating sound independently of the drivers. HDF’s density helps absorb and dissipate vibrational energy, reducing the risk of panel resonance that could otherwise introduce coloration or muddiness to the sound. This property allows for a more accurate reproduction of audio, particularly in the midrange and bass frequencies, where enclosure resonance is most problematic.
Additionally, HDF’s smooth surface finish enables precise machining and tight tolerances during assembly, which is essential for creating airtight joints and minimizing air leaks. This further enhances bass response and overall sound integrity. As a result, many high-end loudspeaker manufacturers select HDF to achieve superior acoustic performance and consistency in their products Bowers & Wilkins, What Hi-Fi?.
Manufacturing Processes: Working with HDF in Loudspeaker Enclosures
The manufacturing process of loudspeaker enclosures using High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) involves several precise and controlled steps to ensure optimal acoustic performance and structural integrity. HDF is favored for its uniform density, smooth surface, and minimal voids, which are critical for reducing unwanted resonance and coloration in speaker cabinets. The process typically begins with the selection and cutting of HDF panels using CNC routers or precision saws, allowing for tight tolerances and repeatability in mass production. This accuracy is essential for ensuring airtight joints and consistent internal volumes, both of which directly impact sound quality.
After cutting, the panels are often machined to include features such as driver cutouts, bracing slots, and cable management channels. Advanced techniques like dado or rabbet joints are commonly employed to enhance the strength and alignment of the enclosure. Adhesives and mechanical fasteners are used in tandem to assemble the panels, with clamping systems ensuring even pressure during curing. The assembled enclosure is then sanded to achieve a smooth finish, which is particularly important for subsequent veneering or painting processes.
HDF’s fine surface allows for high-quality finishes, whether through direct painting or the application of decorative veneers. This not only improves aesthetics but also adds a protective layer against moisture and wear. Throughout the process, manufacturers must control dust and emissions, as HDF machining can release fine particulates and formaldehyde. Compliance with environmental and workplace safety standards, such as those outlined by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, is essential in modern production environments.
Durability and Longevity: HDF’s Resistance to Warping and Wear
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) is highly valued in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing due to its exceptional durability and resistance to warping and wear. Unlike solid wood or lower-density fiberboards, HDF is engineered under intense pressure and heat, resulting in a dense, uniform material with minimal internal voids. This structural integrity is crucial for loudspeaker enclosures, which must maintain precise dimensions and acoustic properties over time. HDF’s high density makes it less susceptible to moisture absorption, a common cause of warping and swelling in wood-based materials. This resistance ensures that enclosures retain their shape and structural stability even in environments with fluctuating humidity levels, thereby preserving sound quality and mechanical performance over the product’s lifespan.
Additionally, HDF’s smooth, hard surface is less prone to dents, scratches, and other forms of wear compared to softer materials. This durability is particularly important for loudspeakers, which may be subject to frequent handling, transportation, or installation in public or commercial spaces. The material’s resilience extends the usable life of the enclosure, reducing the need for repairs or replacements and contributing to the overall reliability of the finished product. Manufacturers often choose HDF for these reasons, as it offers a balance of mechanical strength and long-term stability that supports both the functional and aesthetic requirements of high-quality loudspeaker systems Woodworking Network European Panel Federation.
Cost Analysis: Is HDF a Smart Investment for Manufacturers?
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) for loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing, several factors must be considered. HDF is generally more expensive than standard Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) due to its higher density and more refined manufacturing process. However, its superior mechanical properties—such as increased rigidity and reduced resonance—can translate into better acoustic performance, potentially justifying the higher material cost for premium products.
From a manufacturing perspective, HDF’s uniformity and smooth surface reduce the need for extensive finishing, which can lower labor and finishing material costs. Its machinability is comparable to MDF, allowing for efficient CNC routing and precise assembly, which is crucial for maintaining tight tolerances in loudspeaker design. However, the increased density also means higher tool wear and potentially greater energy consumption during processing, which can incrementally raise operational expenses.
In terms of supply chain, HDF is widely available but may not be as ubiquitous as MDF, potentially leading to regional price fluctuations. Bulk purchasing and long-term supplier agreements can help mitigate these costs. Additionally, the enhanced durability and perceived quality of HDF enclosures can support higher retail pricing, improving profit margins for manufacturers targeting audiophile or high-end markets.
Ultimately, the decision to use HDF hinges on the manufacturer’s target market and product positioning. For brands prioritizing acoustic excellence and premium aesthetics, the investment in HDF can be justified by the potential for superior product performance and higher market value. For more information on material costs and market trends, see Statista and Forest2Market.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Sourcing of HDF
The environmental impact of High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing is a critical consideration, particularly as sustainability becomes a central concern in the audio and furniture industries. HDF is typically produced from wood fibers sourced from both hardwood and softwood species, often utilizing byproducts from sawmills and wood processing operations. This use of residual wood material can reduce waste and promote more efficient resource utilization compared to solid wood alternatives. However, the sustainability of HDF is closely tied to the sourcing of its raw materials. Responsible manufacturers increasingly rely on wood certified by organizations such as the Forest Stewardship Council or the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification, ensuring that forests are managed in an environmentally and socially responsible manner.
Another environmental consideration is the use of adhesives and resins in HDF production, which can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as formaldehyde. Advances in resin technology have led to the development of low-emission or formaldehyde-free HDF panels, which are preferable for both environmental and health reasons. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting these eco-friendly alternatives to comply with regulations and meet consumer demand for greener products (United States Environmental Protection Agency).
End-of-life disposal and recyclability also factor into HDF’s environmental profile. While HDF can be recycled, the presence of adhesives may complicate the process. As a result, some manufacturers are exploring take-back programs and closed-loop recycling systems to minimize landfill waste. Overall, the sustainability of HDF in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing depends on responsible sourcing, advances in low-emission production, and improved end-of-life management.
Case Studies: Brands and Products Leveraging HDF for Superior Audio
Several renowned audio brands have adopted High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) in their loudspeaker enclosure designs, capitalizing on its acoustic and structural advantages. For instance, Bowers & Wilkins utilizes HDF in their flagship 800 Series Diamond speakers, citing the material’s superior density and uniformity as key factors in minimizing cabinet resonance and coloration. Similarly, Dynaudio employs HDF in their Contour series, emphasizing the material’s ability to provide a stable, inert platform for drivers, which translates to clearer, more accurate sound reproduction.
Another notable example is Focal, whose Kanta line features HDF enclosures with internal bracing to further suppress unwanted vibrations. Focal’s engineers highlight that HDF’s fine particle structure allows for precise machining and seamless finishes, enhancing both the acoustic and aesthetic qualities of their products. Additionally, Wharfedale integrates HDF in their Elysian series, leveraging its mass and rigidity to achieve a low-resonance cabinet that supports high-fidelity performance.
These case studies demonstrate that leading manufacturers consistently choose HDF for its ability to deliver superior audio performance, durability, and design flexibility. The widespread adoption of HDF in high-end loudspeakers underscores its status as a material of choice for brands seeking to push the boundaries of sound quality and craftsmanship.
Future Trends: Innovations and Emerging Uses of HDF in Audio Engineering
The future of High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing is shaped by ongoing innovations and the exploration of new applications within audio engineering. As the demand for high-fidelity sound and sustainable materials grows, manufacturers are investing in advanced HDF formulations that offer enhanced acoustic properties, such as improved internal damping and reduced resonance. These advancements are achieved through the integration of nanomaterials and specialized resins, which can further minimize unwanted vibrations and coloration in sound reproduction.
Emerging uses of HDF also include its combination with other composite materials to create hybrid enclosures that balance strength, weight, and acoustic performance. For instance, sandwich constructions using HDF and lightweight cores are being developed to optimize enclosure rigidity while reducing overall mass, a key consideration for portable and professional audio systems. Additionally, digital manufacturing techniques like CNC machining and 3D printing are enabling more complex and precise enclosure geometries, allowing designers to fully exploit the acoustic potential of HDF.
Sustainability is another driving force, with manufacturers seeking to source HDF from certified, renewable wood fibers and employ low-emission adhesives to meet environmental standards. These efforts align with broader industry trends toward eco-friendly product development and lifecycle management. As research continues, it is expected that HDF will play a pivotal role in the next generation of loudspeaker enclosures, offering a blend of acoustic excellence, design flexibility, and environmental responsibility (Woodworking Network, audioXpress).
Conclusion: Is HDF the Future of Loudspeaker Enclosure Manufacturing?
High-Density Fiberboard (HDF) has established itself as a compelling material in the realm of loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing, offering a unique blend of acoustic performance, structural integrity, and cost-effectiveness. Its dense, uniform composition minimizes unwanted resonance and coloration, providing a neutral platform for accurate sound reproduction. Compared to traditional materials like Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF) and plywood, HDF’s superior density and smooth surface allow for precise machining and intricate designs, which are increasingly valued in both high-fidelity and commercial audio markets. Furthermore, HDF’s compatibility with modern finishing techniques and its ability to support complex internal bracing make it attractive for manufacturers seeking both performance and aesthetic flexibility.
However, the future dominance of HDF in loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing is not without caveats. Environmental considerations, such as the use of formaldehyde-based adhesives and the challenges of recycling engineered wood products, may influence material choices as sustainability becomes a greater industry priority. Additionally, while HDF offers excellent acoustic properties, some high-end manufacturers and audiophiles continue to favor solid wood or advanced composites for their unique tonal characteristics and premium appeal.
In conclusion, HDF is poised to play a significant role in the future of loudspeaker enclosure manufacturing, particularly where precision, consistency, and cost are paramount. Its adoption will likely grow alongside advances in sustainable production and finishing technologies. Nevertheless, the material landscape will remain diverse, with HDF complementing rather than wholly replacing other established and emerging materials in the pursuit of optimal loudspeaker performance Audioholics Woodworking Network.
Sources & References
- Wood Panel Industries Federation
- APA – The Engineered Wood Association
- The Wood Database
- The Engineering Toolbox
- Fine Woodworking
- Bowers & Wilkins
- What Hi-Fi?
- European Panel Federation
- Statista
- Forest2Market
- Forest Stewardship Council
- Dynaudio
- Focal
- audioXpress
- Audioholics