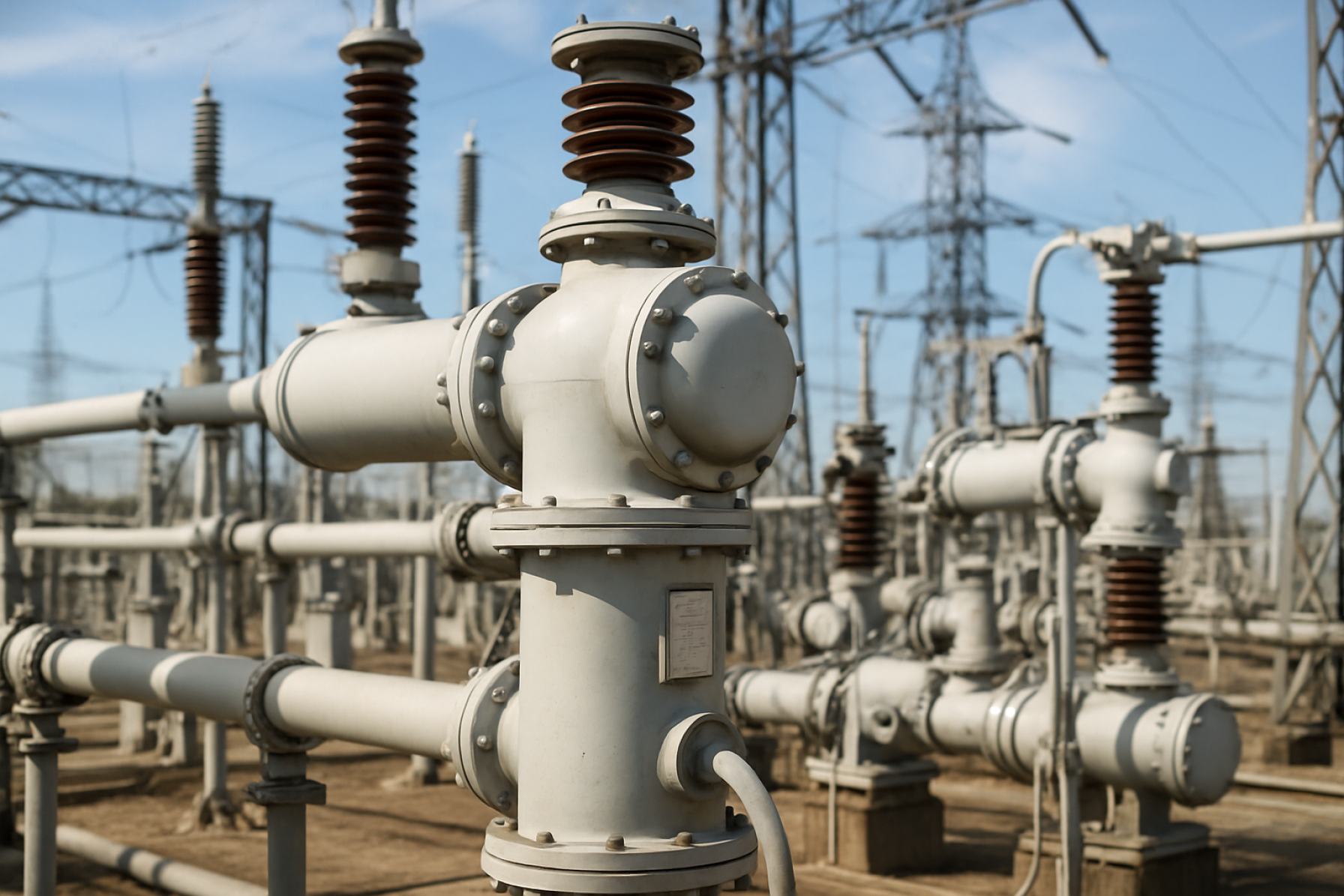
Sulphur Hexafluoride Circuit Breaker Manufacturing in 2025: Navigating Innovation, Regulation, and Global Demand. Discover How This Critical Sector is Shaping the Future of Power Infrastructure.
- Executive Summary: Key Trends and 2025 Outlook
- Global Market Size, Segmentation, and 2025–2030 Growth Forecast
- Technological Innovations in SF6 Circuit Breaker Design
- Regulatory Landscape and Environmental Considerations
- Major Manufacturers and Competitive Landscape (e.g., siemens-energy.com, gegridsolutions.com, abb.com)
- Supply Chain Dynamics and Raw Material Sourcing
- Regional Analysis: Growth Hotspots and Emerging Markets
- Application Sectors: Utilities, Industrial, and Infrastructure
- Challenges: SF6 Emissions, Alternatives, and Compliance
- Future Outlook: Market Opportunities and Strategic Recommendations
- Sources & References
Executive Summary: Key Trends and 2025 Outlook
The manufacturing landscape for Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers is undergoing significant transformation in 2025, shaped by regulatory, technological, and market-driven trends. SF6 circuit breakers have long been the industry standard for high-voltage and extra-high-voltage applications due to their superior arc-quenching properties and compact design. However, the sector faces mounting pressure to address the environmental impact of SF6, a potent greenhouse gas, prompting both innovation and strategic shifts among leading manufacturers.
Key industry players such as Siemens, Hitachi Energy, GE Grid Solutions, and ABB continue to dominate the global market, leveraging extensive R&D capabilities and established supply chains. These companies are actively investing in both the optimization of traditional SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing and the development of alternative technologies. For instance, Siemens and ABB have announced initiatives to reduce SF6 usage and introduce eco-friendly alternatives, reflecting a broader industry trend toward sustainability.
In 2025, regulatory frameworks in Europe and parts of Asia are tightening restrictions on SF6 emissions, compelling manufacturers to enhance gas handling processes and invest in leak detection and recycling systems. The European Union’s F-Gas Regulation, in particular, is a major driver for innovation, pushing manufacturers to accelerate the commercialization of SF6-free solutions while maintaining production of conventional SF6 breakers for markets where alternatives are not yet viable.
Despite these regulatory pressures, demand for SF6 circuit breakers remains robust in regions with expanding power infrastructure, such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and parts of Africa. Utilities and industrial customers in these markets continue to favor SF6 technology for its reliability and cost-effectiveness, ensuring ongoing production and incremental improvements in manufacturing efficiency and quality control.
Looking ahead, the outlook for SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing in the next few years is characterized by a dual-track approach: continued optimization of SF6 breaker production for established markets, alongside accelerated R&D and pilot deployments of alternative technologies. Leading manufacturers are expected to further automate production lines, enhance digital monitoring capabilities, and expand service offerings to support lifecycle management and regulatory compliance. The sector’s evolution will be shaped by the pace of regulatory change, customer adoption of alternatives, and the ability of manufacturers to balance environmental responsibility with operational and economic realities.
Global Market Size, Segmentation, and 2025–2030 Growth Forecast
The global market for sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breaker manufacturing is poised for steady growth from 2025 through 2030, driven by ongoing investments in power transmission and distribution infrastructure, grid modernization, and the increasing demand for reliable high-voltage equipment. SF6 circuit breakers are widely used in medium and high-voltage applications due to their superior arc-quenching properties and compact design, making them a preferred choice for utilities and industrial users worldwide.
As of 2025, the market is segmented by voltage rating (medium voltage, high voltage, and extra-high voltage), application (utilities, industrial, commercial), and geography (Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America). The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, India, and Southeast Asian countries, continues to dominate global demand, fueled by rapid urbanization, grid expansion, and government initiatives to upgrade aging infrastructure. Major manufacturers such as Siemens, Hitachi, ABB, and General Electric maintain significant production facilities and R&D centers in this region, supporting both domestic and export markets.
Europe and North America are also important markets, with a focus on replacing legacy equipment and integrating renewable energy sources. However, these regions are increasingly influenced by environmental regulations targeting SF6 emissions, prompting manufacturers to invest in alternative technologies and improved gas handling systems. Companies such as Siemens and ABB have announced initiatives to develop SF6-free switchgear, but SF6 circuit breakers remain the industry standard for high-voltage applications in the near term.
From 2025 to 2030, the global SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing market is expected to grow at a moderate compound annual growth rate (CAGR), with estimates generally ranging from 4% to 6% annually, depending on region and application. Growth will be underpinned by ongoing electrification, grid reliability requirements, and the expansion of renewable energy projects, particularly in emerging economies. At the same time, the market outlook is shaped by regulatory trends and the gradual introduction of alternative technologies, which may influence product development and investment decisions by leading manufacturers.
- Siemens: A global leader in power transmission and distribution equipment, with a strong portfolio of SF6 circuit breakers and ongoing R&D in eco-friendly alternatives.
- ABB: Major supplier of high-voltage switchgear, including SF6 circuit breakers, with a focus on digitalization and sustainability.
- Hitachi: Key player in the Asian and global markets, offering a range of SF6 circuit breakers for utility and industrial applications.
- General Electric: Provides advanced SF6 circuit breaker solutions and invests in next-generation grid technologies.
Technological Innovations in SF6 Circuit Breaker Design
The manufacturing of sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers is undergoing significant technological innovation in 2025, driven by both performance demands and environmental considerations. SF6 circuit breakers have long been valued for their high dielectric strength and arc-quenching properties, making them essential in medium and high-voltage power transmission and distribution. However, the industry is now focused on enhancing efficiency, digital integration, and sustainability.
One of the most notable trends is the integration of advanced monitoring and diagnostic systems. Leading manufacturers such as Siemens and Hitachi are equipping their SF6 circuit breakers with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and digital communication modules. These systems enable real-time condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote operation, which help utilities reduce downtime and optimize asset management. For example, Siemens has introduced digitalized switchgear solutions that incorporate sensors for continuous SF6 gas density monitoring, temperature, and humidity tracking, ensuring operational reliability and early fault detection.
Material science advancements are also shaping the next generation of SF6 circuit breakers. Manufacturers are developing new contact materials and arc-quenching mechanisms to improve breaker lifespan and reduce maintenance intervals. ABB, a major player in the sector, has focused on optimizing the geometry of interrupter chambers and employing advanced alloys for contacts, which enhances arc extinction and reduces SF6 gas decomposition. These innovations contribute to lower operational costs and improved environmental performance.
Environmental concerns regarding SF6’s high global warming potential are prompting manufacturers to innovate in gas handling and leakage prevention. Companies like GE and Siemens are investing in improved sealing technologies, automated gas filling systems, and enhanced leak detection. These measures are designed to minimize SF6 emissions throughout the product lifecycle, aligning with evolving regulatory requirements and corporate sustainability goals.
Looking ahead, the outlook for SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing in the next few years includes further digitalization, increased automation in production processes, and the gradual introduction of alternative gas technologies. While SF6 remains the industry standard for high-voltage applications in 2025, the sector is actively preparing for a transition to lower-impact solutions, with ongoing R&D investments by industry leaders such as ABB, Siemens, and GE.
Regulatory Landscape and Environmental Considerations
The regulatory landscape for sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breaker manufacturing is undergoing significant transformation in 2025, driven by mounting environmental concerns and evolving international standards. SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential approximately 23,500 times greater than CO2 over a 100-year period. As a result, regulatory bodies worldwide are intensifying scrutiny of its use, particularly in the electrical transmission and distribution sector where SF6 circuit breakers are prevalent.
In the European Union, the revision of the F-Gas Regulation (EU) No 517/2014 is a pivotal development. The updated regulation, expected to be enforced in 2025, proposes stricter controls on the use and emissions of SF6, including potential phase-out schedules for certain applications. This regulatory tightening compels manufacturers to invest in leak detection, improved gas handling, and alternative technologies. Major manufacturers such as Siemens and Hitachi Energy are actively developing and commercializing SF6-free switchgear solutions, anticipating both compliance requirements and market demand for greener alternatives.
In North America, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) continues to monitor SF6 emissions under its Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program. While federal regulations have not yet mandated a phase-out, several states—most notably California—have enacted their own restrictions, including mandatory reporting and limits on SF6 use in new equipment. This patchwork of regulations is prompting manufacturers to standardize best practices and accelerate the adoption of alternative gases or vacuum technologies.
Asia-Pacific markets, led by countries such as China and Japan, are also responding to global environmental pressures. While regulatory frameworks are less uniform, there is a clear trend toward aligning with international standards and reducing SF6 emissions. Companies like Mitsubishi Electric and Toshiba are investing in research and development of eco-efficient circuit breakers, often in collaboration with utilities and government agencies.
Looking ahead, the outlook for SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing is shaped by a dual imperative: ensuring grid reliability while minimizing environmental impact. Regulatory momentum is expected to intensify, with further restrictions and reporting requirements likely in the next few years. Manufacturers are thus prioritizing innovation in SF6-free technologies, lifecycle management, and recycling initiatives to remain competitive and compliant in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
Major Manufacturers and Competitive Landscape (e.g., siemens-energy.com, gegridsolutions.com, abb.com)
The global market for Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers is characterized by the presence of several major manufacturers, each leveraging advanced engineering capabilities and extensive international networks. As of 2025, the competitive landscape is shaped by a combination of technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and a growing emphasis on sustainability due to SF6’s high global warming potential.
Among the leading manufacturers, Siemens Energy stands out for its comprehensive portfolio of high-voltage SF6 circuit breakers, which are widely deployed in transmission and distribution networks worldwide. Siemens Energy has also been at the forefront of developing alternative solutions to SF6, reflecting the industry’s gradual shift toward eco-friendly technologies. Their manufacturing facilities are strategically located to serve key markets in Europe, Asia, and the Americas, ensuring robust supply chain resilience.
Another major player is GE Grid Solutions, a division of General Electric, which manufactures a broad range of SF6 circuit breakers for both primary and secondary substations. GE Grid Solutions is notable for its investment in research and development, particularly in the area of SF6-free alternatives, while continuing to support the installed base of traditional SF6 equipment. Their global manufacturing footprint includes facilities in North America, Europe, and Asia, enabling them to meet diverse regional requirements.
ABB is another key competitor, offering SF6 circuit breakers that are recognized for their reliability and performance in demanding grid environments. ABB’s manufacturing operations are highly automated and integrated, supporting both large-scale production and customization for specific client needs. The company is also actively involved in industry initiatives aimed at reducing SF6 emissions and developing next-generation switchgear technologies.
Other significant manufacturers include Hitachi Energy, which has a strong presence in Asia and Europe, and Mitsubishi Electric, known for its high-voltage circuit breaker solutions and ongoing innovation in gas-insulated switchgear. Both companies are investing in R&D to address environmental concerns and comply with evolving international regulations.
Looking ahead, the competitive landscape is expected to evolve as regulatory pressures mount and utilities increasingly seek alternatives to SF6. Major manufacturers are likely to accelerate the development of eco-efficient technologies while maintaining support for existing SF6 infrastructure, ensuring a dynamic and competitive market environment through 2025 and beyond.
Supply Chain Dynamics and Raw Material Sourcing
The supply chain dynamics and raw material sourcing for Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breaker manufacturing in 2025 are shaped by evolving regulatory, environmental, and geopolitical factors. SF6 circuit breakers, widely used in high-voltage electrical grids, rely on a complex network of suppliers for critical components and gases. The primary raw material, SF6 gas, is a potent greenhouse gas, and its procurement is increasingly scrutinized due to tightening environmental regulations in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia.
Major manufacturers such as Siemens, Hitachi, and ABB are actively engaged in securing reliable sources of high-purity SF6 from global chemical producers. These companies often source SF6 from specialized gas suppliers with operations in regions like East Asia, where production capacity is concentrated. For example, Air Liquide and Linde are among the leading industrial gas suppliers providing SF6 to circuit breaker manufacturers worldwide. The supply chain for SF6 is sensitive to fluctuations in raw material prices, transportation costs, and regulatory changes, particularly as the European Union and other jurisdictions consider stricter controls or phase-outs of SF6 in new equipment.
In addition to SF6 gas, the manufacturing process requires high-grade metals (such as copper and aluminum for contacts and conductors), insulating materials (ceramics, epoxy resins), and precision-engineered mechanical components. These materials are sourced from a global network of suppliers, with quality and traceability being paramount due to the safety-critical nature of circuit breakers. Companies like Siemens and ABB have established robust supplier qualification programs and digital supply chain management systems to mitigate risks related to material shortages or quality issues.
Looking ahead to the next few years, the supply chain for SF6 circuit breakers is expected to face increasing pressure from both environmental policy and market demand for alternatives. Manufacturers are investing in R&D for SF6-free technologies, but the installed base and ongoing demand for SF6 equipment in developing regions will sustain the need for reliable sourcing. Strategic partnerships with gas suppliers, investment in recycling and reclamation of SF6, and enhanced traceability systems are likely to become more prominent as the industry adapts to a changing regulatory and market landscape.
Regional Analysis: Growth Hotspots and Emerging Markets
The global landscape for sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breaker manufacturing in 2025 is characterized by dynamic regional shifts, with growth hotspots emerging in both established and developing markets. Asia-Pacific continues to dominate production and consumption, driven by rapid urbanization, grid modernization, and expanding renewable energy integration. China, in particular, remains the world’s largest market and manufacturing hub for SF6 circuit breakers, supported by major domestic players such as TBEA and CHINT Group. These companies benefit from robust government investments in ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission projects and ongoing upgrades to the national grid.
India is another significant growth hotspot, with increasing demand for reliable power infrastructure and a strong push towards electrification in rural and urban areas. Leading Indian manufacturers, including Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) and CG Power and Industrial Solutions, are expanding their SF6 circuit breaker production capacities to meet both domestic and export requirements. Southeast Asian nations, notably Vietnam and Indonesia, are also witnessing rising investments in transmission and distribution networks, creating new opportunities for regional and international suppliers.
In Europe, the market is shaped by stringent environmental regulations and a gradual shift towards alternative technologies. However, SF6 circuit breakers remain prevalent in high-voltage applications due to their proven reliability. Key manufacturers such as Siemens and ABB (now part of Hitachi Energy) continue to serve the region, while also investing in research for eco-friendly alternatives. Germany, France, and the UK are focal points for both manufacturing and innovation, with ongoing grid reinforcement projects sustaining demand through 2025.
North America, led by the United States and Canada, is experiencing moderate growth, primarily fueled by grid modernization initiatives and the replacement of aging infrastructure. Major players like General Electric and Eaton maintain a strong presence, supplying SF6 circuit breakers for utilities and industrial applications. The region is also seeing increased regulatory scrutiny regarding SF6 emissions, prompting manufacturers to enhance gas handling and recycling capabilities.
Looking ahead, emerging markets in the Middle East and Africa are poised for accelerated growth, underpinned by large-scale electrification projects and investments in power generation. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa are expanding their transmission networks, attracting global suppliers and fostering local manufacturing partnerships. As these regions prioritize grid reliability and capacity expansion, demand for SF6 circuit breakers is expected to remain robust through the next several years.
Application Sectors: Utilities, Industrial, and Infrastructure
Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breakers remain a critical component in high-voltage electrical systems, with their application spanning utilities, industrial operations, and infrastructure projects. As of 2025, the manufacturing and deployment of SF6 circuit breakers are shaped by both the enduring technical advantages of SF6 and the evolving regulatory and sustainability landscape.
In the utilities sector, SF6 circuit breakers are widely used for transmission and distribution networks, particularly at voltages above 72.5 kV. Their superior arc-quenching properties and compact design make them the preferred choice for substations and grid interconnections. Major manufacturers such as Siemens, Hitachi Energy, and GE Grid Solutions continue to supply SF6 breakers to utilities worldwide, supporting grid modernization and expansion projects. For example, Siemens has highlighted the ongoing demand for SF6 technology in regions where alternatives are not yet fully established, especially in fast-growing power markets.
In industrial applications, SF6 circuit breakers are integral to the protection of large-scale manufacturing plants, mining operations, and heavy industries that require reliable high-voltage switching. The chemical, oil & gas, and metals sectors, in particular, rely on the high interrupting capacity and low maintenance needs of SF6 breakers. Companies such as ABB and Eaton manufacture and supply these breakers for industrial substations and process plants, often customizing solutions to meet specific operational and safety requirements.
The infrastructure sector—including railways, airports, and large commercial complexes—also utilizes SF6 circuit breakers for reliable power distribution and protection. The compactness of SF6 breakers is particularly advantageous in urban infrastructure projects where space is at a premium. Siemens and Schneider Electric are among the key suppliers addressing these needs, often integrating SF6 breakers into turnkey substation solutions.
Looking ahead, while the application sectors continue to rely on SF6 circuit breakers for their proven performance, manufacturers are increasingly investing in research and development of alternative technologies due to environmental concerns over SF6’s high global warming potential. Nevertheless, in 2025 and the next few years, SF6 circuit breakers are expected to maintain a significant presence in utilities, industrial, and infrastructure sectors, especially in regions where regulatory transitions to alternatives are gradual and where operational demands necessitate the unique properties of SF6.
Challenges: SF6 Emissions, Alternatives, and Compliance
Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breaker manufacturing faces mounting challenges in 2025, primarily due to the environmental impact of SF6 emissions, the search for viable alternatives, and tightening regulatory compliance. SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential approximately 23,500 times greater than CO2 over a 100-year period. As a result, manufacturers are under increasing scrutiny from both regulators and customers to minimize emissions throughout the product lifecycle.
The European Union’s F-Gas Regulation, revised in 2024, is a key driver of change, setting stricter limits on the use and handling of SF6 in electrical equipment. The regulation mandates phased reductions in SF6 usage and requires manufacturers to implement leak detection, reporting, and recovery systems. Similar regulatory trends are emerging in other regions, including North America and parts of Asia, compelling global manufacturers to adapt their processes and product portfolios accordingly.
Major industry players such as Siemens, Hitachi Energy, and GE Vernova are investing heavily in research and development to address these challenges. These companies are actively developing and commercializing alternative technologies, such as vacuum circuit breakers and gas-insulated switchgear using fluoronitrile-based or CO2-based mixtures, which offer similar performance to SF6 but with significantly lower environmental impact. For example, Siemens has introduced its “Blue” portfolio, which utilizes clean air as an insulating medium, while Hitachi Energy and GE Vernova have launched products using alternative gas mixtures.
Despite these advances, the transition away from SF6 is not without obstacles. Technical challenges include ensuring the reliability, safety, and compactness of alternative solutions, especially for high-voltage applications. Additionally, the existing installed base of SF6 equipment remains substantial, necessitating robust end-of-life management and retrofitting strategies to prevent emissions during maintenance and decommissioning.
Looking ahead, the outlook for SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing is shaped by a dual imperative: meeting the immediate needs of grid operators for reliable high-voltage switching, while accelerating the shift toward environmentally sustainable technologies. Manufacturers are expected to continue investing in innovation, supply chain adaptation, and compliance systems to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape and support the global transition to low-carbon power infrastructure.
Future Outlook: Market Opportunities and Strategic Recommendations
The future outlook for sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) circuit breaker manufacturing in 2025 and the coming years is shaped by a complex interplay of regulatory, technological, and market-driven factors. SF6 circuit breakers have long been the industry standard for high-voltage and extra-high-voltage applications due to their superior arc-quenching properties and compact design. However, the sector is now at a pivotal juncture as environmental concerns and regulatory pressures intensify.
A key driver influencing the market is the global push to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. SF6 is recognized as a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential thousands of times greater than CO2. Regulatory bodies in Europe and other regions are tightening restrictions on SF6 use, prompting manufacturers to accelerate research into alternative technologies and eco-friendly solutions. Leading manufacturers such as Siemens, Hitachi Energy, and GE Grid Solutions are investing heavily in the development of SF6-free switchgear and circuit breakers, leveraging alternative gases and vacuum technologies.
Despite these trends, the installed base of SF6 circuit breakers remains substantial, particularly in Asia-Pacific and emerging markets where grid expansion and modernization projects are ongoing. In 2025, demand for SF6 circuit breakers is expected to persist in regions where regulatory frameworks are less stringent or where the cost and technical maturity of alternatives remain barriers. Major suppliers such as ABB and Mitsubishi Electric continue to support both conventional SF6 and next-generation products, ensuring a dual-track approach to market needs.
Strategically, manufacturers are advised to:
- Accelerate R&D into SF6-free technologies to future-proof product portfolios and comply with evolving regulations.
- Expand service offerings for maintenance, monitoring, and end-of-life management of existing SF6 assets, capitalizing on the large installed base.
- Forge partnerships with utilities and grid operators to pilot and validate alternative solutions, building credibility and market readiness.
- Monitor regional policy developments closely, especially in the EU and North America, to anticipate shifts in demand and compliance requirements.
In summary, while SF6 circuit breaker manufacturing will remain relevant in the near term, the sector’s long-term growth and competitiveness will increasingly depend on innovation, regulatory agility, and proactive engagement with the global energy transition.
Sources & References
- Siemens
- Hitachi Energy
- GE Grid Solutions
- ABB
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Toshiba
- Siemens Energy
- GE Grid Solutions
- Air Liquide
- Linde
- CHINT Group
- CG Power and Industrial Solutions
- Eaton